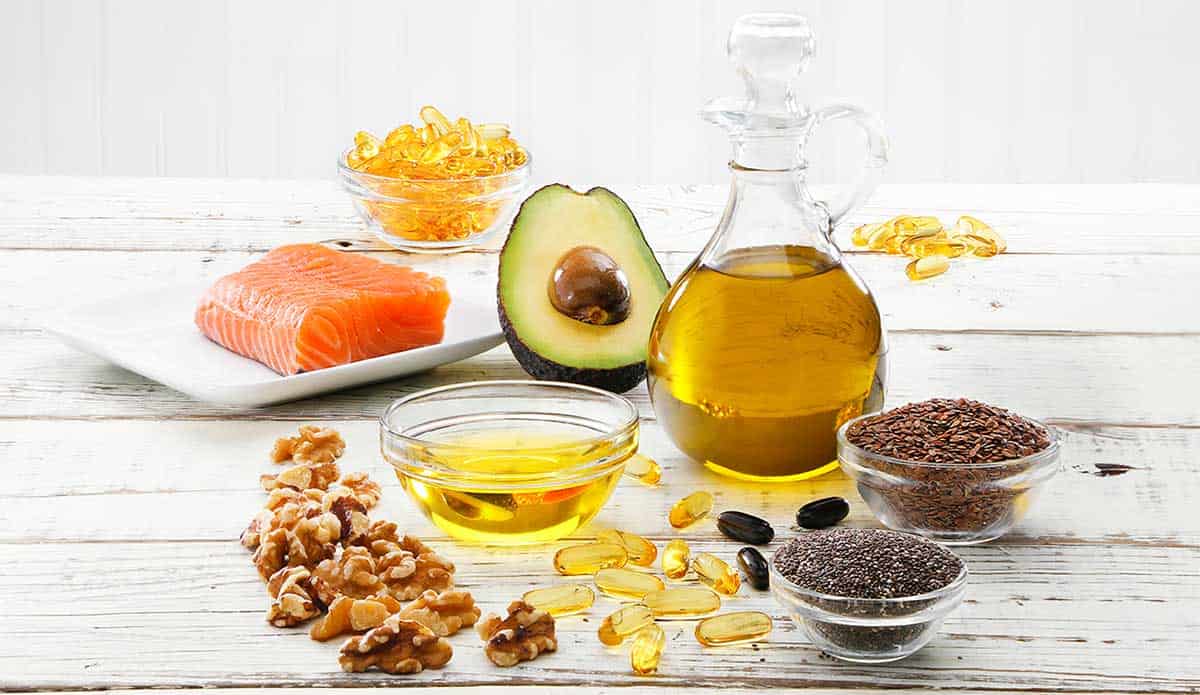

Fuel your body with nourishing fats!
Essential to life, omega oils are a type of polyunsaturated fat that the body needs to function properly. These healthy fats are used to store energy in the body, transport fat-soluble vitamins through the blood, regulate blood cholesterol levels, and help maintain healthy skin and hair.Your body can make most fats from raw materials through your diet, except two, omega-3 fats called linolenic acid (ALA) and omega-6 fats called linoleic acid (LA). These two fatty acids must be consumed through your diet. The predominant sources of omega-3s are EPA and DHA (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) which have been extensively researched for their health benefits and are mostly found in fish.
Alternative sources of omega-3s can be found in walnuts, flax and chia seeds if fish is not a part of your diet. Your body can efficiently convert ALA to EPA but it’s conversion from ALA to DHA is limited. Algae contains a good source of DHA and can be found in supplement form. It can also be found mixed with flax and other oils.
Sources of omega-6 can be found in meats, nuts, seeds, legumes, grains and vegetable oils. Although you need omega-6 in your diet, foods such as red meat and vegetable oils like cottonseed and soybean should be consumed in moderation. Evening primrose oil, black currant oil, and borage oil are great sources of omega-6 and are sold in supplement form.
It’s important to consume the right balance of omega-3 to omega-6. Some experts suggest a 1:1 or 1:2 ratio. A typical western diet consumes too much omega-6, up to 14–25 times more than omega-3s. Researchers believe this imbalance leads to a variety of mental disorders, an increased risk of heart disease and other inflammatory health conditions.
Heart health
Clinical evidence suggests that EPA and DHA can help reduce risk factors for heart disease. They can reduce inflammation in your blood vessels and lower triglycerides and cholesterol, a type of fat in your bloodstream that builds plaque in your arteries, leading to cardiovascular disorders. The average intake of DHA and EPA in the U.S. is about 100–200 milligrams per day, far below the 500 milligrams that many experts recommend for healthy individuals.1 Salmon has the highest concentration of DHA of any fish source as it contains approximately 1,000–1,500 milligrams per 3-ounce serving. The USDA suggests consuming two servings of 3 ounces at least twice a week. Reducing dietary saturated fat from animal sources and replacing it with polyunsaturated fats found in fish and vegetables can help keep your arteries free from plaque and may protect you from many chronic diseases like coronary heart disease.Brain health
Essential fatty acids are the most critical components to boosting brainpower. Your brain is made up of approximately 60 percent fat and DHA is the most prominent fat in the brain. Most researchers agree that DHA plays a vital role in managing behavior, mood, memory and brain development. Currently, researchers are studying the effectiveness of DHA for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), depression, autism and Asperger’s syndrome. Your brain is the most energy-demanding of all the human body organs and ensuring optimal amounts of DHA can have profound effects on cognitive thinking, learning and behavior. Experts suggest that healthy adults should consume between 1,000–3,000 milligrams of fish oil daily to protect your cognitive and neurological health. For healthy brain and eye development it’s suggested that infants consume 100 milligrams per day of DHA and for children aged 2–4, 150 milligrams is suggested.2Eye health
Your eyes have a special need for DHA as it’s a component of the retina, the part of the eyes that processes visual images so you can see. DHA helps maintain better eye health across your lifespan. In fact, low levels of DHA are associated with eye disease, especially as you age. Furthermore, DHA improves fluidity, flexibility, and functionality of eye tissues and cells.Skin health
The secret to healthy skin is to start from the inside out. Omega oils deliver the basic nutrition for your skin cells to develop and be healthy. Internally they influence your cell’s ability to hold water and allow nutrients and waste to pass in and out of the cells. As an extra bonus, this moisturizing effect can help to keep your skin wrinkle-free.Coconut oil
Coconut oil has many health benefits but it does not contain omega-3 essential fatty acids. Learn more about Coconut Oil.1 Nichols, Peter D., James Petrie, and Surinder Singh. “Long-Chain Omega-3 Oils–An Update on Sustainable Sources.” Nutrients 2.6 (2010): 572–585. PMC. Web. 23 Nov. 2015. 2 Aranceta J and Perez-Rodrigo C. Recommended dietary reference intakes, nutritional goals and dietary guidelines for fat and fatty acids: a systematic review. Br.J.Nutr. 2012;107 Suppl 2:S8-22.

 VIEW ALL
VIEW ALL



